A Java variable is a piece of memory that can contain a data value. A variable
thus has a data type. Data types are covered in more detail in the text on Java data types.
Variables are typically used to store information which your Java program needs to do its job. This can be any
kind of information ranging from texts, codes (e.g. country codes, currency codes etc.) to numbers, temporary
results of multi step calculations etc.
In the code example below, the
main() method contains the declaration of a single integer variable named
number. The value of the integer variable is first set to 10, and then 20 is added to the variable
afterwards.
public class MyClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int number = 10;
number = number + 20;
}
}
Types of Variable
There are three types of variables in java:
- local variable
- instance variable
- static variable
1) Local Variable
A variable which is declared inside the method is called local variable.
2) Instance Variable
A variable which is declared inside the class but outside the method,
is called instance variable . It is not declared as static.
3) Static variable
A variable that is declared as static is called static variable. It cannot be local.
class A{
int data=50;//instance variable
static int m=100;//static variable
void method(){
int n=90;//local variable
}
}//end of class
int data=50;//instance variable
static int m=100;//static variable
void method(){
int n=90;//local variable
}
}//end of class
A non-static field is a variable that belongs to an object. Objects keep their internal state in non-static fields.
Non-static fields are also called instance variables, because they belong to instances (objects) of a class.
Non-static fields are covered in more detail in the text on Java fields.
A static field is a variable that belongs to a class. A static field has the same value for all objects that
access it. Static fields are also called class variables. Static fields are also covered in more detail in the
text on Java fields.
A local variable is a variable declared inside a method. A local variable is only accessible inside the method
that declared it. Local variables are covered in more detail in the text on Java methods.
A parameter is a variable that is passed to a method when the method is called. Parameters are also only accessible
inside the method that declares them, although a value is assigned to them when the method is called. Parameters
are also covered in more detail in the text on Java methods.
Java Variable Declaration
Exactly how a variable is declared depends on what type of variable it is (non-static, static, local, parameter).
However, there are certain similarities that
In Java you declare a variable like this:
type name ;
Instead of the word
type, you write the data type of the variable. Similarly, instead
of the word name you write the name you want the variable to have.
Here is an example declaring a variable named
myVariable of type int.
int myVariable;
Here are examples of how to declare variables of all the primitive data types in Java:
byte myByte;
short myShort;
char myChar;
int myInt;
long myLong;
float myFloat;
double myDouble;
Here are examples of how to declare variables of the object types in Java:
Byte myByte;
Short myShort;
Character myChar;
Integer myInt;
Long myLong;
Float myFloat;
Double myDouble;
String myString;
Notice the uppercase first letter of the object types.
When a variable points to an object the variable is called a "reference" to an object. I will get back
to the difference between primitive variable values and object references in a later text.
The rules and conventions for choosing variable names are covered later in this text.
Java Variable Assignment
Assigning a value to a variable in Java follows this pattern:
variableName = value ;
Here are three concrete examples which assign values to three different variables with different data types
myByte = 127;
myFloat = 199.99;
myString = "This is a text";
The first line assigns the byte value 127 to the byte variable named
myByte.
The second line assigns the floating point value 199.99 to the floating point variable named myFloat.
The third line assigns the String value (text) this is a text to the String variable named
myString.
You can also assign a value to a variable already when it is declared. Here is how that is done:
byte myByte = 127;
float myFloat = 199.99;
String myString = "string value";
Data Types in Java
Data types represent the different values to be stored in the variable. In java, there are two types of data types:
- Primitive data types
- Non-primitive data types
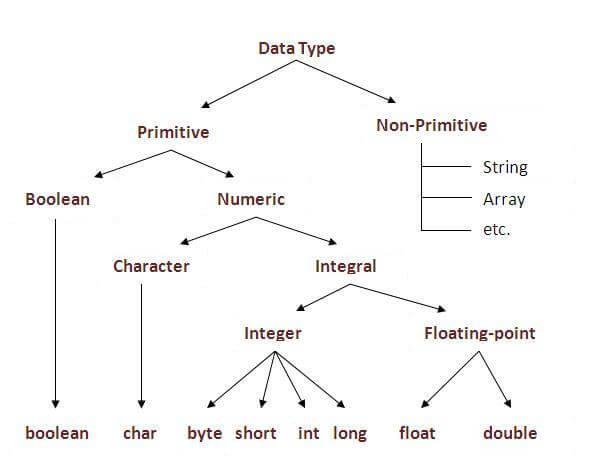
Data Type and Default Value
| boolean | false | 1 bit |
| char | '\u0000' | 2 byte |
| byte | 0 | 1 byte |
| short | 0 | 2 byte |
| int | 0 | 4 byte |
| long | 0L | 8 byte |
| float | 0.0f | 4 byte |
| double | 0.0d | 8 byte |
No comments:
Post a Comment